EPON and GPON are two common fiber access technologies. They use optical fiber to transmit data, providing users with high-speed, high-bandwidth internet access services. EPON is based on Ethernet technology, while GPON utilizes the ITU-T G.984 standard. These two technologies have significant differences in architecture and operating principles, making them more suitable for different application scenarios.
content
EPON
Uplink
Downlink
GPON
Uplink
Downlink
10G EPON
Uplink
Downlink
10G GPON
Uplink
Downlink
With the growing demand for digitalization, 10G EPON and 10G GPON OLTs have emerged, providing stronger support for high-bandwidth, low-latency applications. The emergence of these two technologies marks the continuous evolution of the fiber access field and lays a solid foundation for the development of a future digital society.
EPON
Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON) is a fiber access network based on Ethernet technology. Its core concept is to transmit data over optical fiber, while using a passive optical network, eliminating the need to provide power to devices distributed throughout the network. EPON uses a point-to-multipoint topology, with the optical line terminal (OLT) as the core device and the optical network unit (ONU) as the user-side device.
The EPON architecture consists of the OLT, ONUs, and optical distribution network (ODN). The OLT is the core of the network, responsible for managing overall network traffic and communicating with the ONUs. The ONU, located at the user end, is an optical interface device responsible for converting user-side data into optical signals. The ODN is the optical distribution network used to transmit optical signals between different OLTs and ONUs.
Uplink
When a user device sends data, the ONU converts the data into an optical signal and transmits it to the OLT via the ODN. The OLT receives the optical signal, converts it into an electrical signal, and transmits the data to the core network.
Downlink
The OLT receives data from the core network, converts it into an optical signal, and transmits it to the corresponding ONU via the ODN. The ONU receives the optical signal, converts it into an electrical signal, and delivers the data to the user's terminal device.
EPON has a wide range of applications in real-world networks, playing a key role in urban broadband access, enterprise networks, and mobile base station backhaul. For example, in urban broadband access, EPON can provide high-speed, stable network connections, meeting users' demands for high bandwidth. In enterprise networks, EPON can deliver reliable data transmission by simplifying network structure and improving transmission efficiency. Furthermore, in mobile base station backhaul, EPON can be used to quickly and reliably transmit large amounts of data, supporting the development of mobile networks.
GPON
Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) is a fiber-optic access technology that uses the ITU-T G.984 standard. Compared to EPON, GPON offers higher data rates and more robust performance. GPON also utilizes a point-to-multipoint topology, with the optical line terminal (OLT) and optical network unit (ONU) at its core.
GPON's architecture, similar to EPON, consists of the OLT, ONU, and optical distribution network (ODN). The OLT, as the core switching device, manages the entire network and communicates with the ONU. The ONU, as the user-end device, converts user data into optical signals. The ODN is the distribution network used to transmit the optical signals.
Uplink
When user devices send data, the ONU converts it into an optical signal and transmits it to the OLT via the ODN. The OLT receives the optical signal, converts it into an electrical signal, and transmits the data to the core network.
Downlink
The OLT receives data from the core network, converts it into an optical signal, and transmits it to the corresponding ONU via the ODN. The ONU receives the optical signal, converts it into an electrical signal, and delivers the data to the user terminal.
GPON is also widely used in real-world networks. In large-scale networks, GPON provides higher bandwidth and more stable connections, meeting users' demand for high-speed networks. In business environments, GPON's high performance makes it an ideal choice for enterprise networks, supporting efficient data transmission and communication. GPON also excels in delivering multimedia content and video conferencing, providing users with a richer network experience.
10G EPON
10G EPON is a high-speed version of EPON technology designed to meet networks with higher bandwidth requirements. It utilizes symmetrical uplink and downlink rates of 10 Gbps, offering greater data transmission capacity than traditional EPON. The basic concepts of 10G EPON retain the core principles of EPON, but improve transmission speeds to adapt to growing digital demands.
The architecture and components of 10G EPON are similar to those of traditional EPON, including the OLT, ONU, and ODN. However, 10G EPON equipment requires higher processing power and greater bandwidth to handle high-speed data transmission and processing.
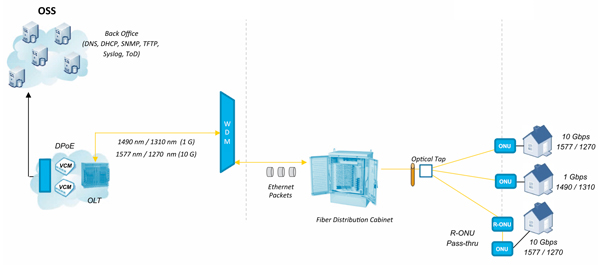
Uplink
When a user device sends high-speed data, the ONU converts it into a 10 Gbps optical signal and transmits it to the OLT via the ODN. The OLT receives the optical signal, converts it into an electrical signal, and transmits the high-speed data to the core network.
Downlink
The OLT receives high-speed data from the core network, converts it into a 10 Gbps optical signal, and transmits it to the corresponding ONU via the ODN. The ONU receives the optical signal, converts it into an electrical signal, and delivers the high-speed data to the user terminal device.
10G EPON is widely used in scenarios with strict high-bandwidth requirements, such as data center interconnection, large-scale enterprise networks, and high-speed broadband access. In data centers, 10G EPON supports the rapid transmission of large amounts of data, meeting the demands of cloud computing and big data applications. In large-scale enterprise networks, 10G EPON provides high-performance connectivity, supporting enterprise-class applications and large-scale data transmission. In high-speed broadband access, 10G EPON offers users faster and more reliable network connections, meeting the urgent needs of modern users for high-bandwidth services.
10G GPON
10G GPON is a high-speed evolution of GPON technology, designed to provide greater bandwidth and improved performance. Compared to traditional GPON, 10G GPON utilizes symmetrical uplink and downlink rates of 10 Gbps, providing users with faster data transmission capabilities. This makes 10G GPON an ideal choice for high-density users, large-scale data transmission, and symmetrical service requirements.
The architecture and components of 10G GPON are similar to those of traditional GPON, including the OLT, ONU, and ODN. However, 10G GPON requires higher processing power and bandwidth to support high-speed data transmission and processing.
Uplink
When a user device sends high-speed data, the ONU converts it into a 10 Gbps optical signal and transmits it to the OLT via the ODN. The OLT receives the optical signal, converts it into an electrical signal, and transmits the high-speed data to the core network.
Downlink
The OLT receives high-speed data from the core network, converts it into a 10 Gbps optical signal, and transmits it to the corresponding ONU via the ODN. The ONU receives the optical signal, converts it into an electrical signal, and delivers the high-speed data to the user terminal.
10G GPON has a wide range of applications in real-world networks, particularly in scenarios requiring high-density, high-speed transmission. In densely populated areas such as city centers and commercial districts, 10G GPON can provide high-speed, reliable internet access to a large number of users. In large enterprise networks, 10G GPON supports large-scale data transmission and provides high-performance network connectivity. 10G GPON also excels in areas such as mobile base station backhaul and video surveillance, providing strong support for a variety of application scenarios.
Summary
This article provides a detailed introduction to EPON, GPON, 10G EPON, and 10G GPON. EPON and GPON are two different fiber-optic transmission technologies, both based on PON (Passive Optical Network) technology. PON is a fiber-based network technology that uses a single optical fiber to transmit signals to multiple users. The optical fiber terminal (OLT) is a crucial component of a PON network, connecting the ISP's core network and the user's optical network unit (ONU) device. The OLT's primary function is to convert the ISP's data into optical signals and send them to the ONU device. The OLT also manages all devices in the PON network, including the ONU and optical distribution network (ODN) equipment. 10G EPON and 10G GPON are upgraded versions of EPON and GPON, offering higher bandwidth and faster speeds. 10G EPON and 10G GPON operate similarly to EPON and GPON, but they use higher frequencies and more complex modulation techniques to achieve higher bandwidth and speeds. 10G EPON and 10G GPON also support more users and longer transmission distances. The OLT plays the same role in 10G EPON and 10G GPON networks as it does in EPON and GPON networks.



