Acute diarrhea is a common illness, often caused by infection, and typically resolves on its own within a few days. However, Dr. Li Biao, a consultant gastroenterologist at Gutcare Gastroenterology Clinic at Parkway East Hospital, warns that in certain situations, patients should seek medical attention immediately.
In an interview with our newspaper's "Live Well" program, Dr. Li Biao pointed out that common infections that cause acute diarrhea include viruses such as norovirus and rotavirus, as well as bacteria such as E. coli.
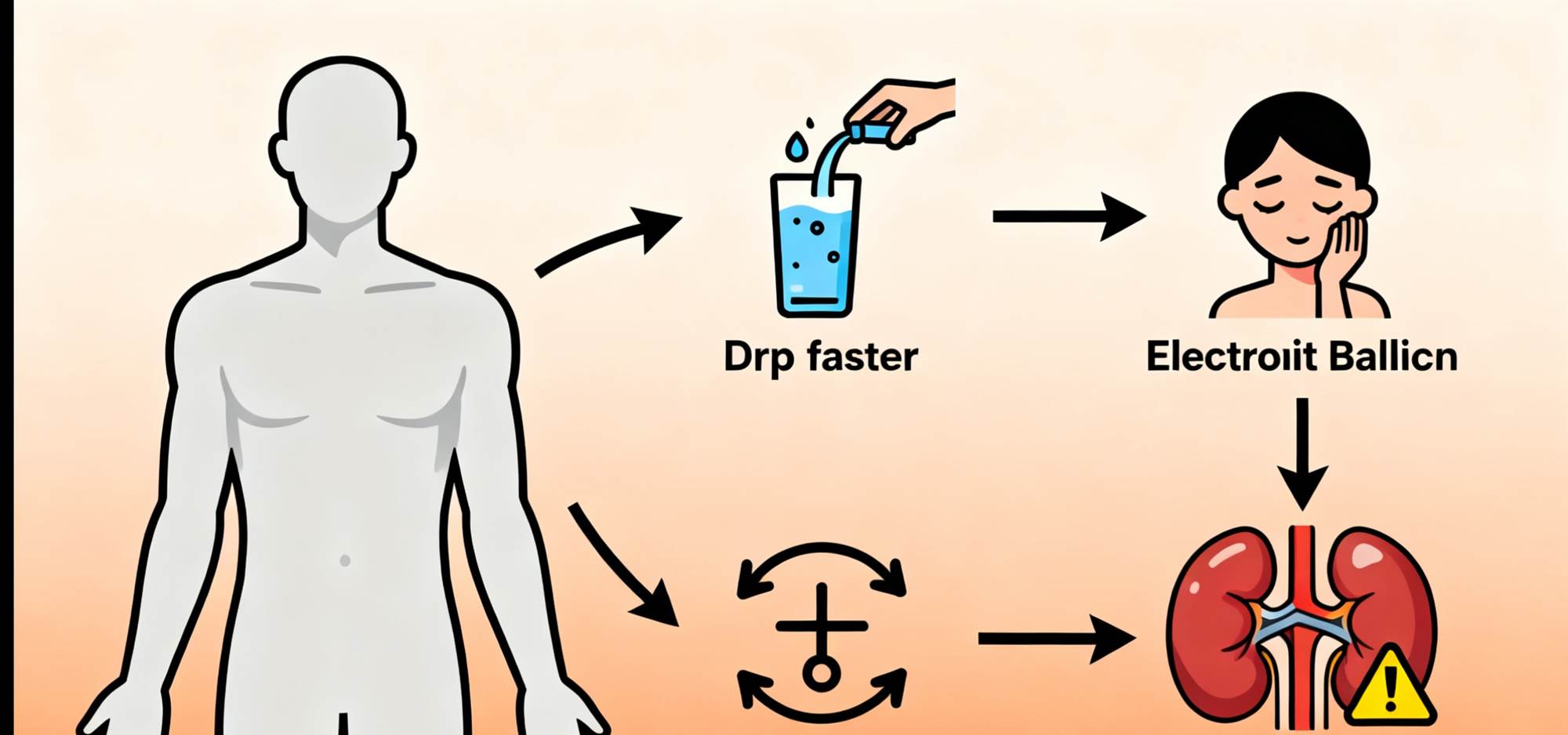
While most cases are mild, persistent or chronic diarrhea can lead to more serious problems such as dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and even, in extreme cases, kidney failure.
He advises seeking medical attention promptly if the following signs and symptoms occur:
■ Persistent dehydration, such as thirst, decreased urine output, and sunken eyes;
■ Severe nausea and vomiting;
■ Inability to eat;
■ Severe abdominal pain;
■ Bloody or black stools;
■ High fever over 39°C;
■ Elderly patients or those with multiple medical conditions
Dr. Lee added that infections are the main cause of diarrhea, and frequent handwashing is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of viruses and bacteria.
It is recommended to wash hands before and after preparing and eating food, as well as after handling raw meat, using the toilet, changing diapers, sneezing, coughing, or blowing your nose. Wash hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
If you are outdoors and don't have access to clean water, use hand sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol.